The water cycle is also known as the "hydrologic cycle" Precipitation When too much water has condensed, the water droplets in the clouds become too big and heavy for the air to hold them And so they fall back down to Earth as rain, snow, hail or sleet, aThis Hydrologic Cycle recycles the earth's valuable water supply In other words, the water keeps getting reused over and over Just think, the next glass of water you drink could have been part of a dinosaur's bath in the Mesozoic Era one hundred million years ago Water in that glass of water could have been a liquid, a solid, and a gasNature regulates itself in a cyclic manner Their are various cycles of nature like water cycle, hydrological cycle, carbon cycle, oxygen cycle, nitrogen cyc
5 C The Natural Spheres The Hydrologic Cycle
What are the 6 stages of the hydrologic cycle
What are the 6 stages of the hydrologic cycle- The water cycle or hydrologic cycle describes the complex systems that allow water to move across the Earth and atmosphere The most basic step of the water cycle is the change of state of water as a liquid, gas or solid in the atmosphere However, the water cycle also envelops various methods of water transportation and water types such as The hydrologic cycle is the process, powered by the sun's energy, which moves water between the oceans, the sky, and the land We can start our examination of the hydrologic cycle with the oceans, which hold over 97% of the planet's water The sun causes evaporation of water on the surface of the ocean The water vapor rises and condenses into
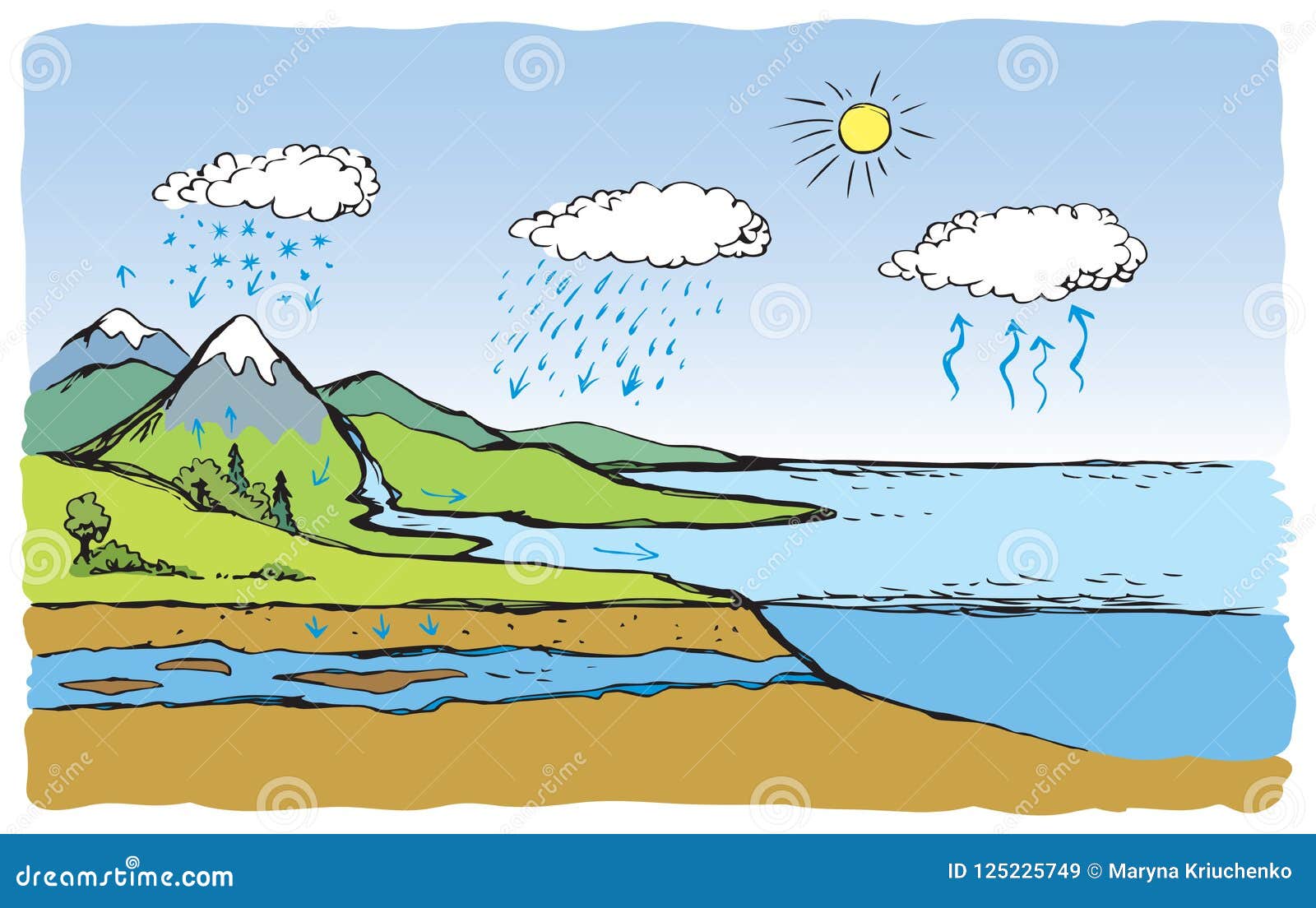




Vector Schematic Water Cycle In Nature Stock Vector Illustration Of Liquid Ground
Well, of course the answer is due to the hydrological cycle The hydrological cycle is a cycle that describes the velocity of water on earth Earth's water experiences a cycle that makes the availability will never used up eventhough it's used daily in huge amount We will study the hydrological cycle components and the explanation belowHydrological Cycle works more actively in the equatorial region that in polar region (6) With the help of Hydrological Cycle, hydrological Budget in any country or the amount of rain, the change of seasons and the nature of the plants etc Directly or indirectly control the amount of water deposited on the surface of the earth (8 The explanation for these model results is that changes in the overall intensity of the hydrologic cycle are controlled not by the availability of
Figure 2 The Hortonian hydrological cycle5 The hydrologic cycle can thus be considered a social construction, which has a definite history and which was produced in a specific scientific and political context in the early 1930s The diagram itself was an important contribution to our modern understanding of the nature of waterRelated Science Earth's water is always in movement, and the natural water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle, describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth Water is always changing states between liquid, vapor, and ice, with these processes happening in the blink of an eye and over millions The answer is certainly because of the hydrological cycle The hydrological cycle is a cycle that describes the rotation of water that exists on Earth Water on Earth experiences a cycle so that its availability cannot be exhausted even though it is used in large quantities daily The hydrological cycle that exists on Earth will be studied below
Hydrologic cycle is the process of transfer of moisture from the atmosphere to the earth in the form of precipitation, conveyance of the precipitated water by streams and rivers to ocean and lakes etc, and evaporation of water back to the atmosphere The hydrologic cycle consist of following processes Evaporation and TranspirationThe hydrological cycle is usually called a recurring consequence of different forms of movement of water and changes of its physical state in the nature on a given area of the Each type rarely occurs alone in nature, but some may dominate under certain conditionsDistillation vs Hydrologic Cycle Let's begin by comparing a home distillation unit to mother nature's own purification system;




Info Sheet Humans And The Water Cycle We Are Becoming Increasingly Aware Of Our Impacts On Nature But Unfort Water Cycle Earth Science Hydrological Cycle




The Water Cycle For Schools
The Hydrologic Cycle The hydrologic cycle attempts to model the storage and movement of water between the biosphere, atmosphere, lithosphere, and the hydrosphere (Figure 5c1) Water on this planet can be stored in any one of the following reservoirs atmosphere, oceans, lakes, rivers, soils, glaciers, snowfields, and groundwaterDefinition and Scope of Hydrology Hydrology is the science that deals with all aspects of the water available on the earth It includes study of occurrence of water, its properties, its distribution and circulation and also its effects on the living beings and their surroundings The hydrologic cycle describes the circulation of water from the ocean and other watery surfaces to the atmosphere and to the landA major source of atmospheric water vapor is evaporation from the oceans Precipitation — rain, snow, sleet or freezing rain — falls from clouds and is a loss of atmospheric water as it removes water from the atmosphere Continue reading →




Water Cycle Hd Stock Images Shutterstock




Water Cycle Definition Steps Diagram Facts Britannica
Nature recycles the earth's water supply through a process known as the water cycle or hydrologic cycle This cycle operates continuously and receives energy from the sun The hydrologic cycle consists of inflows, outflows, and storage Inflows add water to the different parts of the hydrologic system, while outflows remove water The hydrologic cycle is made up of water in all three of its forms solid, liquid and gas The hydrosphere is the area which contains all the water in the atmosphere Every cycle occurs in five different stages Dew is a smaller version of the hydrologic cycle The hydrologic cycle starts in the evaporation stage We propose that this shift may have coincided with the onset of a modern hydrological cycle owing to the rapid emergence of continental crust with nearmodern average elevation and aerial extent
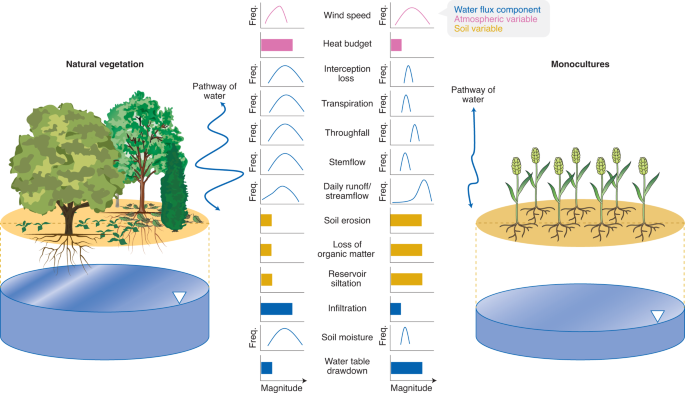



Homogenization Of The Terrestrial Water Cycle Nature Geoscience




Water Cycle In Nature Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock
Earth's mountain regions with their mixed biodiversity are an essential and vital part of the global water cycle "Seasonal snow cover and glaciers store large amounts of freshwater and are therefore critical components of the land surface hydrologic cycle" (USGCRPThe hydrologic cycle Water in Nature – Our world is covered by 70% water Of that water only 25% is fresh water, the rest is saline and ocean based The water cycle describes how water is exchanged (cycled) through Earth's land, ocean, and atmosphere Water always exists in all three places, and in many forms—as lakes and rivers, glaciers and ice sheets, oceans and seas, underground aquifers, and vapor in the air and clouds Evaporation, Condensation, and Precipitation




What Is Water Cycle Describe The Water Cycle In Nature Also Draw A Labelled Sketch To Show The Brainly In



Kelly Brenner The Hydrologic Cycle
The hydrologic cycle is the planet's cleansing system, removing dust from the atmosphere and flushing streams and rivers clean It is also critical to all aspects of life as it is responsible for the breakdown and movement of nutrients and therefore the most important geologic processThe hydrologic cycle involves water moving from the surface (most importantly the oceans) to the atmosphere, across the land, and everywhere in between Environmental scientists know that the hydrologic cycle includes various processes that change water from solid to liquid to gas form and transport it to every corner of earth's surface (and below) In Abstract The uncertainties in assessing the effects of globalscale perturbations to the climate system are due primarily to an inadequate understanding of the hydrological cycle—the cycling of



Earth Floor Cycles




Draw And Explain Water Cycle Occurs In Nature Brainly In
A fundamental characteristic of the hydrologic cycle is that it has no beginning an it has no end It can be studied by starting at any of the following processes evaporation, condensation, precipitation, interception, infiltration, percolation, transpiration, runoff, and storage The hydrological cycle and its influence on climate The uncertainties in assessing the effects of globalscale perturbations to the climate system are due primarily to an inadequate understanding of the hydrological cyclethe cycling of water in the oceans, atmosphere and biosphere Overcoming this problem necessitates new ways of regarding a The water cycle in nature/hydrological cycle is nothing but the circulation of water between the various spheres – earth, air, living organisms, soils and hydrosphere Water moves between them, changing the state of liquid from solid to solid or gaseous, from gaseous to solid or liquid and from solid to liquid or gas
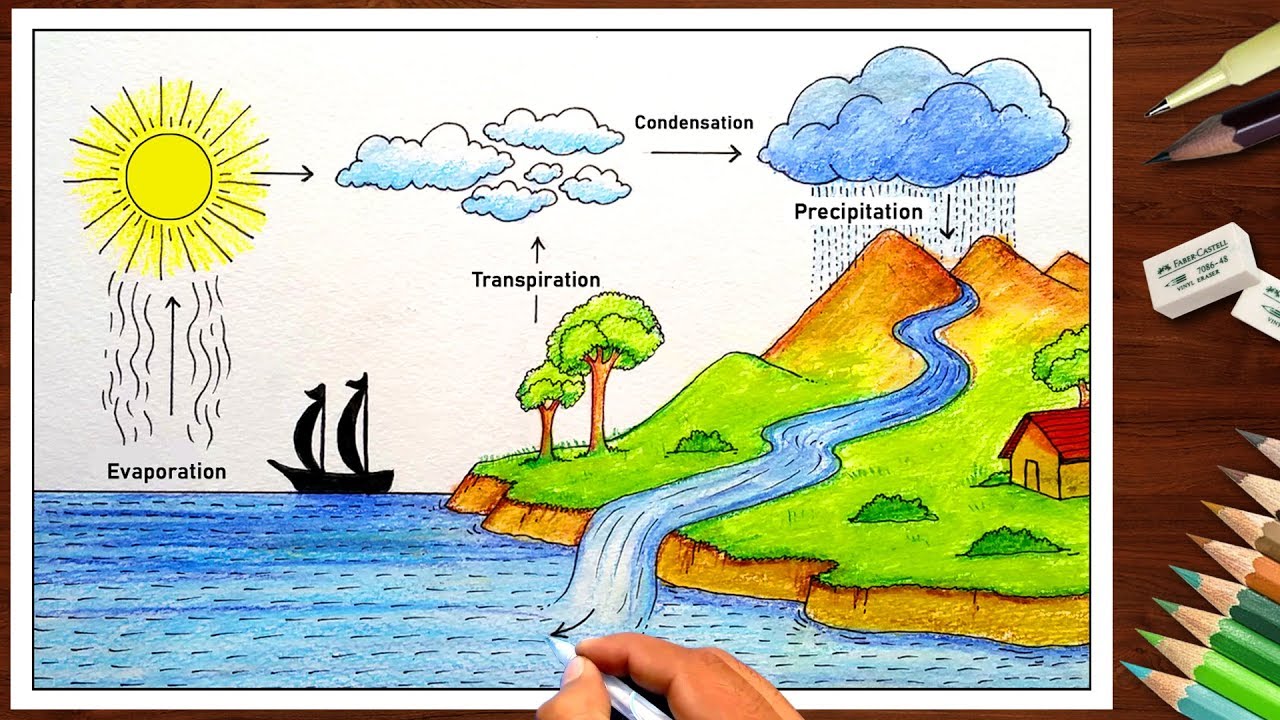




How To Draw Water Cycle Drawing For Beginners Very Easy Step By Step Diagram Youtube
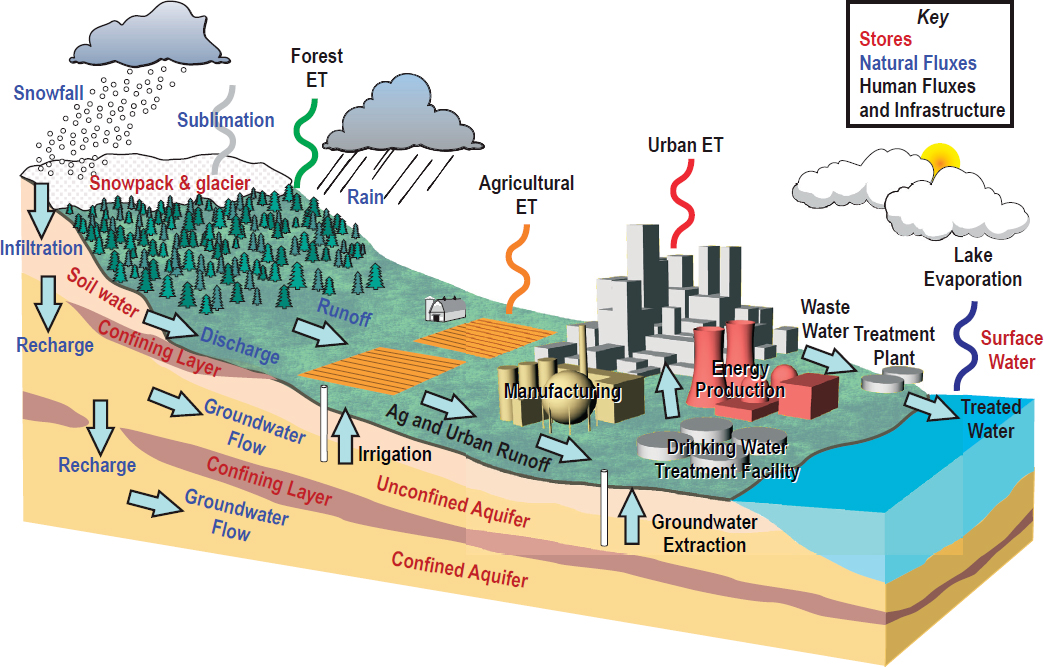



6 Global Hydrological Cycles And Water Resources Thriving On Our Changing Planet A Decadal Strategy For Earth Observation From Space The National Academies Press
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the EarthThe mass of water on Earth remains fairly constant over time but the partitioning of the water into the major reservoirs of ice, fresh water, saline water (Salt Water) and atmospheric water is This is consistent with data 4, 11 indicating an intensifying hydrologic cycle in large regions increasing precipitation leads to increasing surface runoff and soil wetness, which inThe hydrologic cycle plays an important role by ensuring the availability of water for all living organism, including plants, animals, humans and other living species The hydrologic cycle, greatest natural processes, which plays a significant role by a continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth




Hydrological Cycle High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Vector Schematic Representation Of The Water Cycle In Nature Hydrological Cycle Isometric Infographics Illustration Tasmeemme Com
Incorporating a hydrologic cycle by diffusing moisture horizontally fails to take into account the importance of lifting and cooling of air parcels However, more sophisticated idealized models incorporating more dynamical processes 14 show considerable promise The hardsnowball state provides an example of a yet colder climateHydrologic Cycle The water, or hydrologic, cycle describes the pilgrimage of water as water molecules make their way from the Earth's surface to the atmosphere and back again, in some cases to below the surfaceVector schematic water cycle in nature Hydrologic eco energy cyclic precipitation concept on white paper background Freehand line black ink hand drawn school Water Cycle Vector diagram Hydrologic or H2O transformation chart representation of movement phases liquid, ice, gas by physical processes of evapo
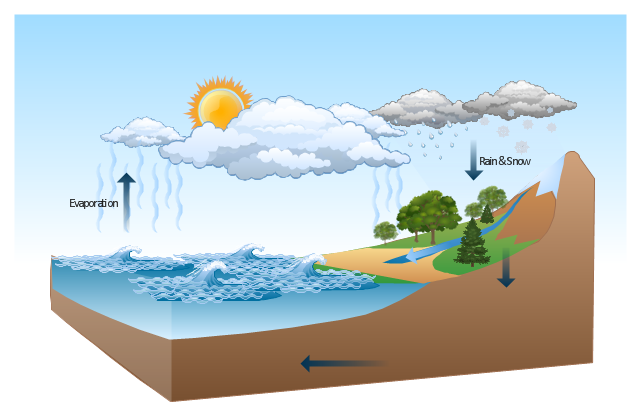



Water Cycle Drawing A Nature Scene Beauty In Nature Illustrations And Clipart Hydrologic Cycle




Vector Schematic Representation Of The Water Cycle In Nature Hydrological Cycle Stock Vector Vector And Low Budget Royalty Free Image Pic Esy Agefotostock
The hydrological cycle creates fresh water from the salty stuff of the oceans, because the salt is left behind when sea water evaporates Much of the water vapour simply falls as rain back into theHow Nature Recycles And Purifies Water Precipitationis one of the most familiar parts ofthe hydrologic cycle Precipitation that falls on theland surface enters into many pathways of the hydrologic cycle When precipitation builds up on the soil surface,The hydrological cycle can be best exemplified pictorially as shown in Fig 11 From the above discussion it is clear that the rain in hot regions and snow in cold regions are the primary sources of water Subsequently they give rise to other sources of




Hydrosphere The Water Cycle Britannica



5 C The Natural Spheres The Hydrologic Cycle
At a cost of more than $105 billion and with a 35 year timeline, this is the largest hydrologic restoration project ever undertaken in the United States Everglades National Park currently is involved in the Central Everglades Planning Project, a fasttrack planning effort for the next generation that will, when authorized by Congress HYDROLOGIC CYCLE is the series of conditions through which water changes from vapor in the atmosphere through precipitation upon land surface or water surfaces and ultimately back into the atmosphere as a result of evaporation and transpirationThe hydrological cycle of the earth is the sum total of all processes in which water moves from the land and ocean surface to the atmosphere and back in form of precipitation The hydrological cycle is dependent on various factors and is equally affected by oceans and land surfaces




The Water Cycle National Geographic Kids




A Comprehensive Study Of The Natural Water Cycle
The Water Cycle Because Earth's water is present in all three states, it can get into a variety of environments around the planet The movement of water around Earth's surface is the hydrologic (water) cycle (figure 2) Figure 2 Because it is a cycle, the water cycle has no beginning and no end Most of Earth's water is stored in theHydrologic Cycle To understand, we need to turn to the Hydrologic Cycle called the water cycle) is the process that moves water around the earth The cycle starts with the sun heating water in our rivers, lakes and oceans and turning it into water vaporThe natural water cycle moves water from the Earth to the atmosphere and back again Water is continually moving through the natural water cycle Earth has exactly the same amount of water as it had thousands of years ago This cycle is also called the hydrological cycle We modify and manage part of the natural water cycle to provide humans



1



Simple Water Cycle Coloring Page Free Printable Coloring Pages
The Global hydrologic cycle is one of the most important natural cycles that operates on Earth It describes the circulation of water through the atmosphere, the land, and the oceans This cycle consists of set of storages (snow, soil moisture, and groundwater) and fluxes (precipitation, evapotranspiration, and runoff) that link the storages



Water Cycle National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration



The Journey Of Water And Our Lives



The Hydrologic Cycle Earth Science Visionlearning




Hydrological Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
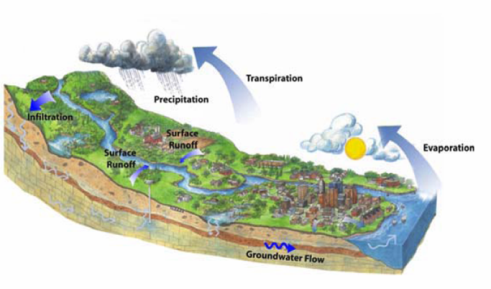



Natural Water Balance Sustainable Technologies Evaluation Program Step
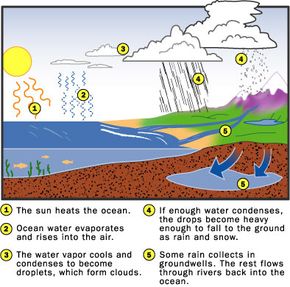



The Cycle Of Rain Howstuffworks
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/NWSjetstream-hydro2010-574cfd2b5f9b58516562ceb5.jpg)



The Importance Of The Water Cycle
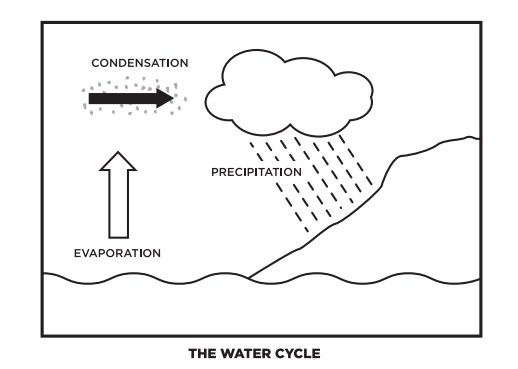



Pop Bottle Water Cycling Terrarium Science World
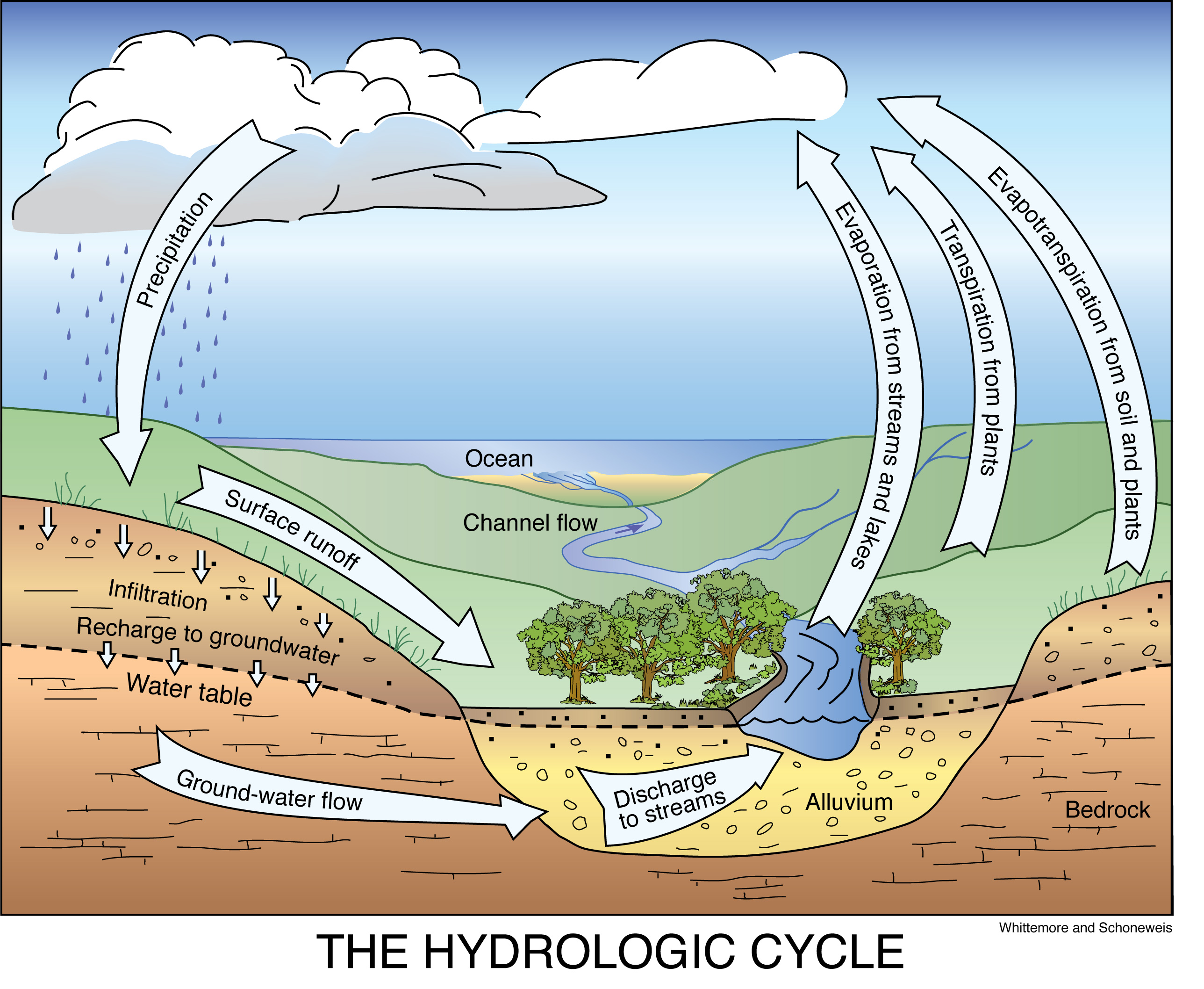



The Hydrologic Water Cycle Geokansas
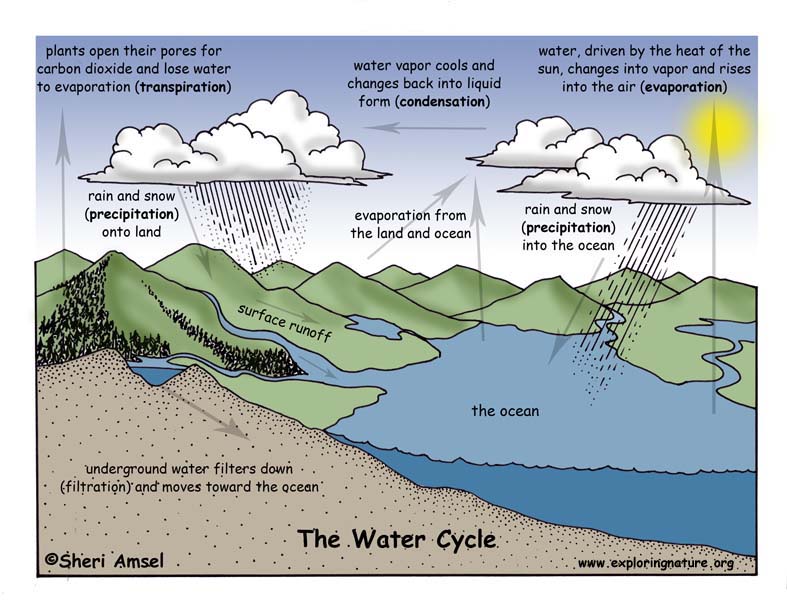



Water Cycle
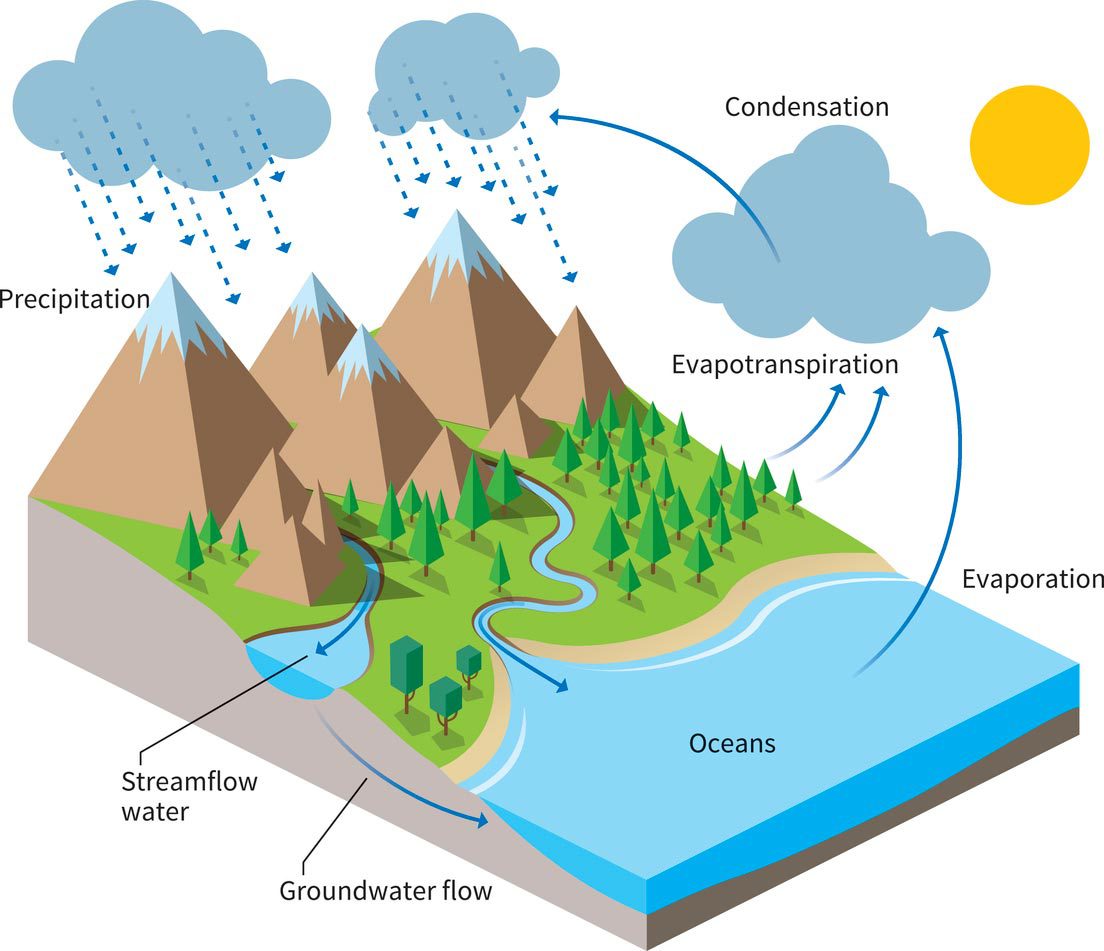



Water Cycle North Penn Water Authority
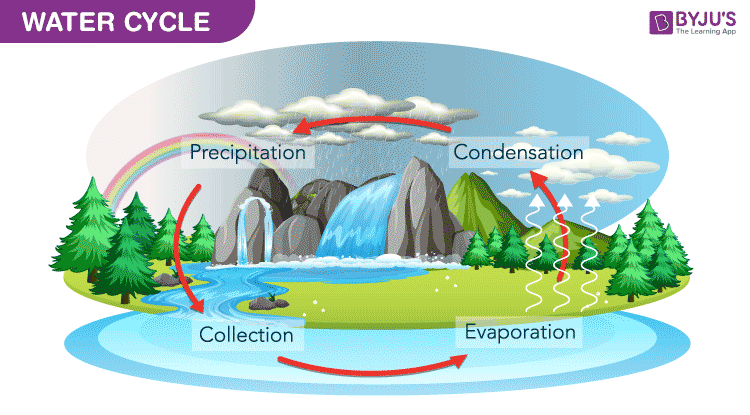



Water Cycle A Diagram Of Water Cycle With Detailed Explanations




Water Cycle Hd Stock Images Shutterstock
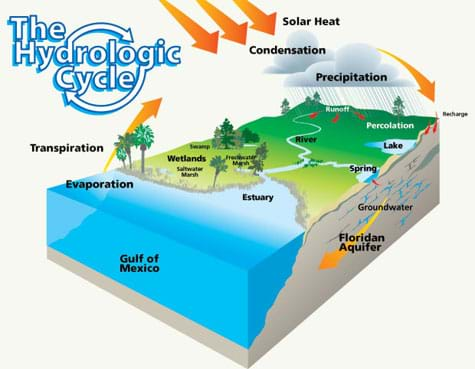



Natural And Urban Stormwater Water Cycles Lesson Teachengineering



1




The Water Cycle National Geographic Society
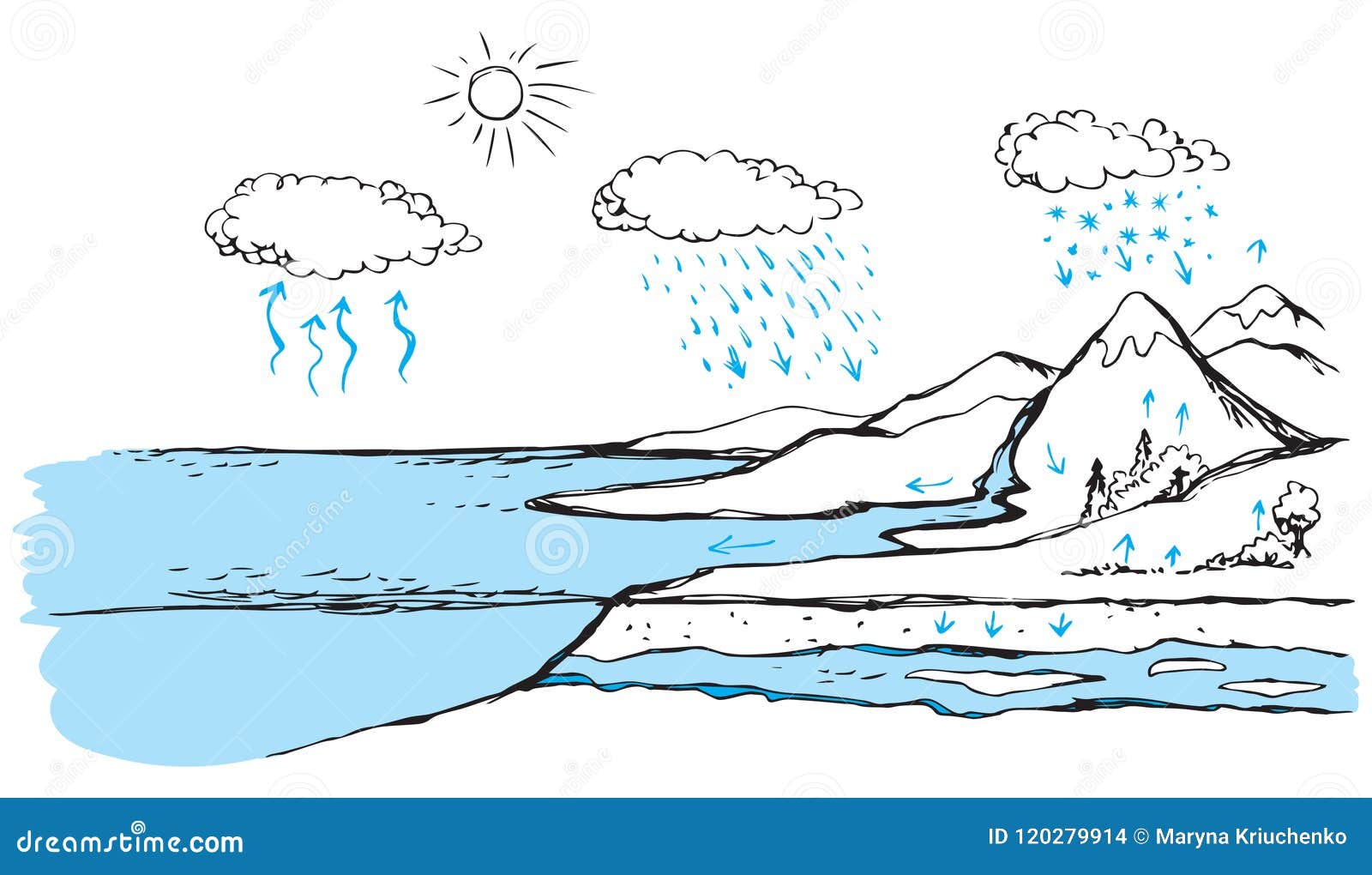



Vector Schematic Water Cycle In Nature Stock Vector Illustration Of Condensation Diagram
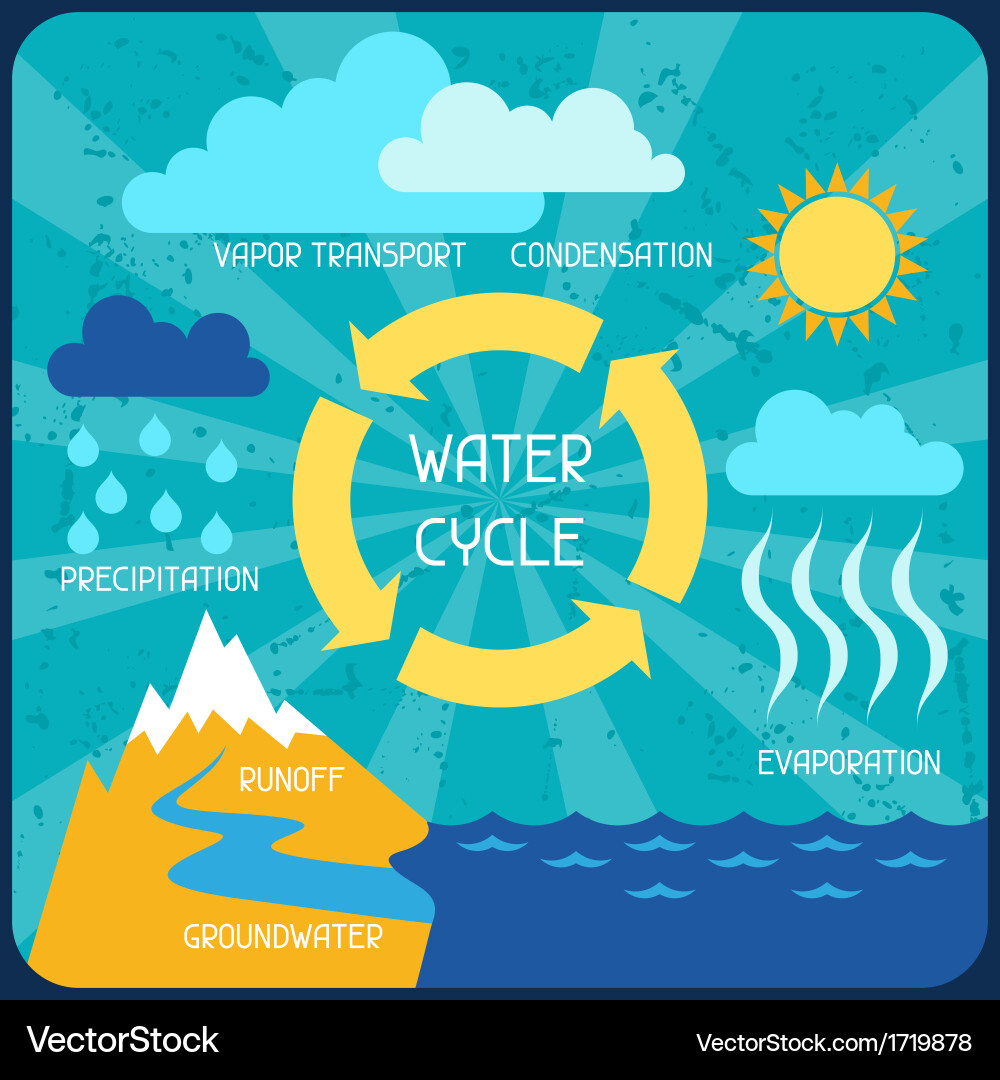



The Water Cycle Poster With Nature Infographics In




Water Cycle In Nature Circulation Cycle And Water Condensation Earth Hydrologic Process Diagram Environmental Circulation Canstock




Missouri Department Of Natural Resources
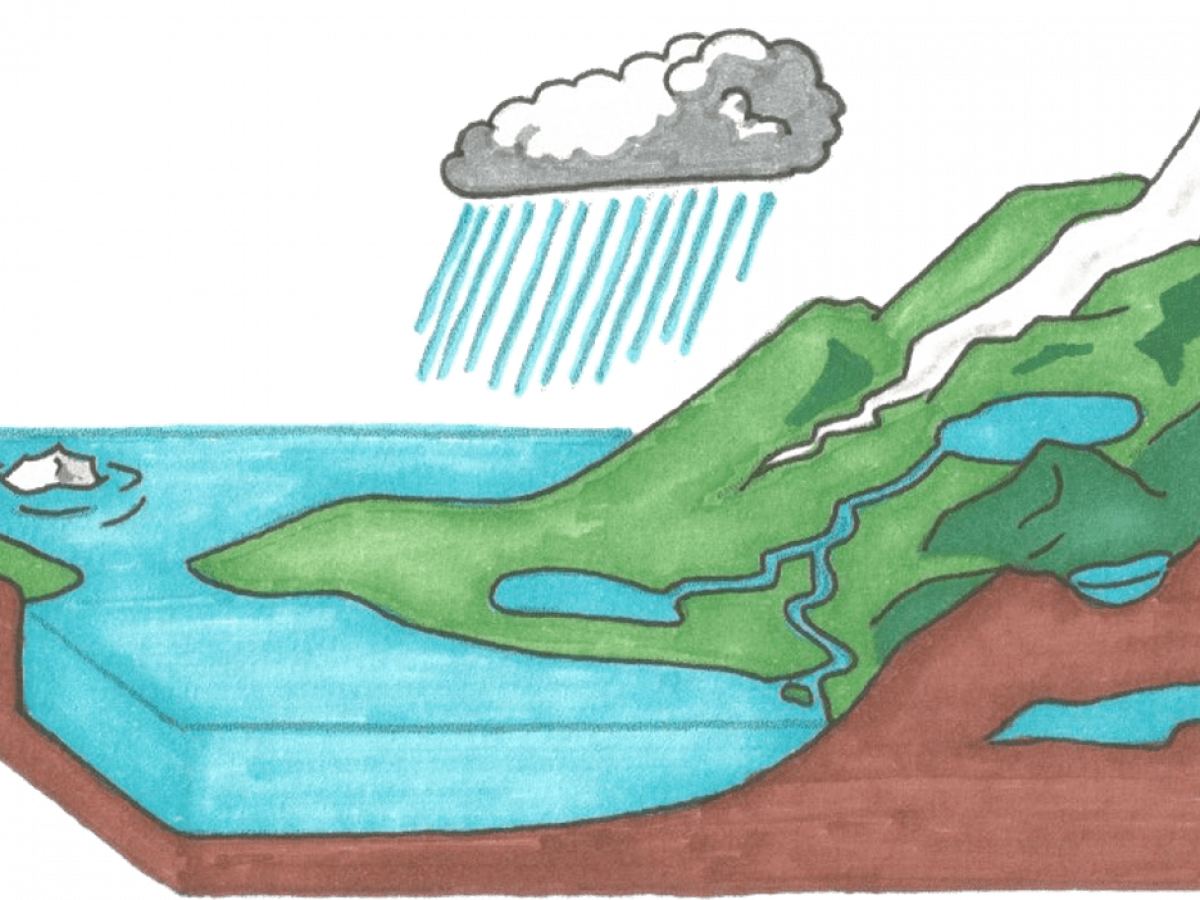



10 Water Cycle Facts Nature Science Experiments More Facts Net
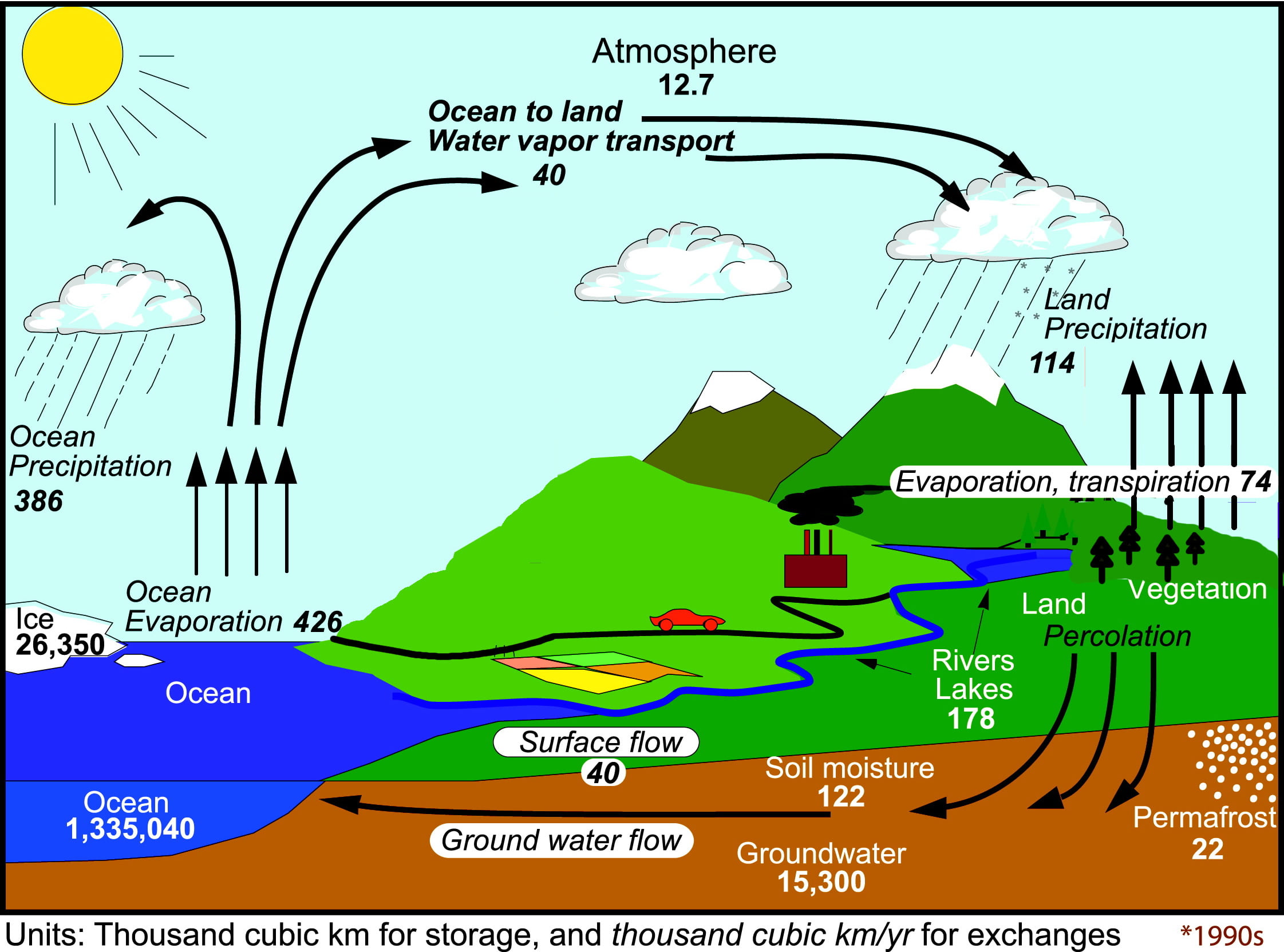



Metlink Royal Meteorological Society The Changing Water Cycle




Global Hydrological Cycles And World Water Resources Science




853 Best Water Cycle Diagram Images Stock Photos Vectors Adobe Stock
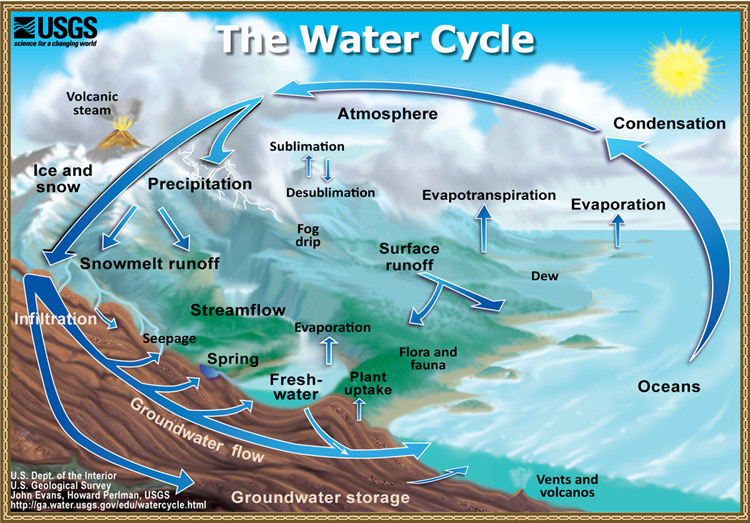



Hydrologic Cycle Energy Education
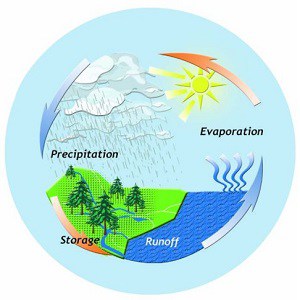



10 Water Cycle Facts Nature Science Experiments More Facts Net




Hydrologic Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Hydrologic Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




The Hydrologic Cycle Where Are The People The Anthropo Scene




Hydrologic Cycle And Interactions




Fun Water Cycle Facts For Kids




The Water Cycle Poster With Nature Infographics In




Water Cycle Wikipedia




How To Draw Water Cycle In Easy Way Learn How To Draw




Vector Schematic Representation Of The Water Cycle In Nature Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image
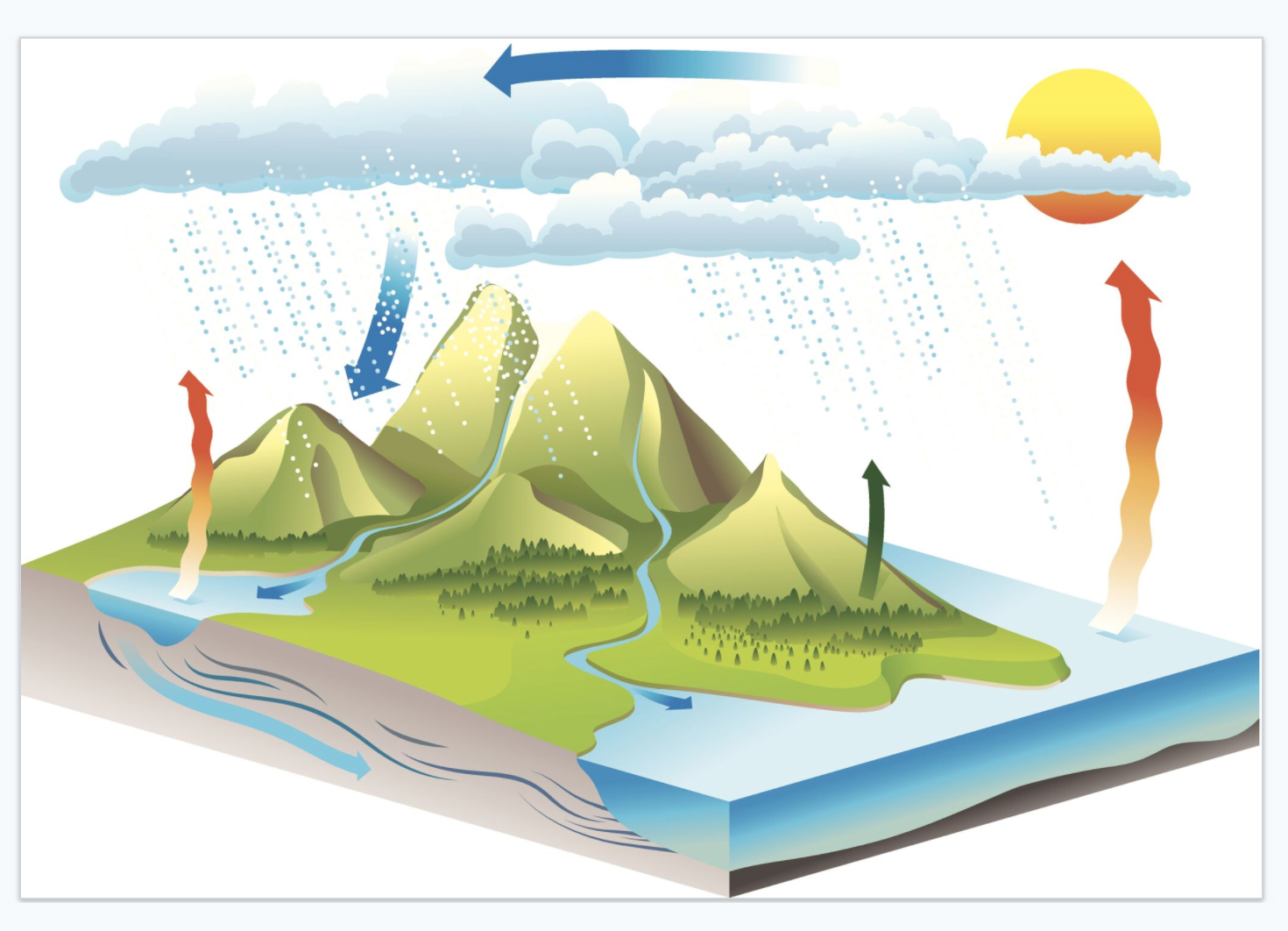



The Water Cycle Science Games Legends Of Learning




Hydrologic Cycle Diagram Water Cycle Water Cycle Project Hydrology



Hydrological Cycle European Environment Agency




Vector Schematic Water Cycle In Nature Stock Vector Illustration Of Liquid Ground



Q Tbn And9gcsiinvun1g6eyl8sox6dn25fx F8zdqsj6hj7iikudmxw5w2 Gx Usqp Cau




Science Of Water Cycle In Nature Schematic Representation Of The Water Cycle Circulation Cycle And Water Condensation Canstock
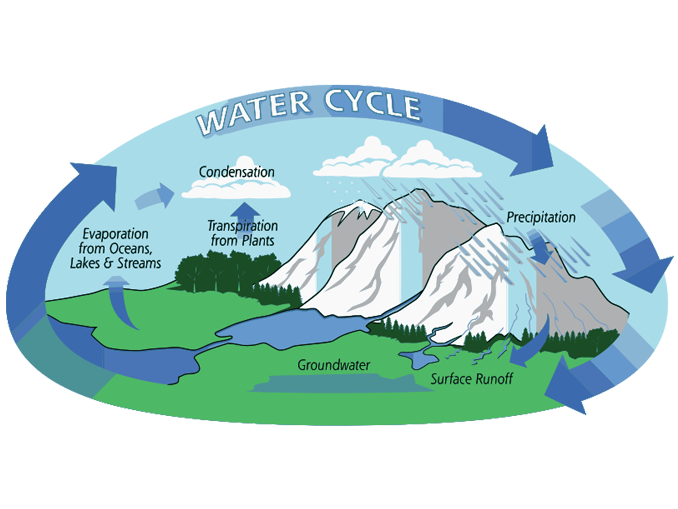



What Is The Hydrologic Cycle 3 Steps Of The Water Cycle Earth How




67 Hydrologic Cycle Vector Images Free Royalty Free Hydrologic Cycle Vectors Depositphotos



Ielts Writing Task 1 Water Cycle Essay Ielts Simon
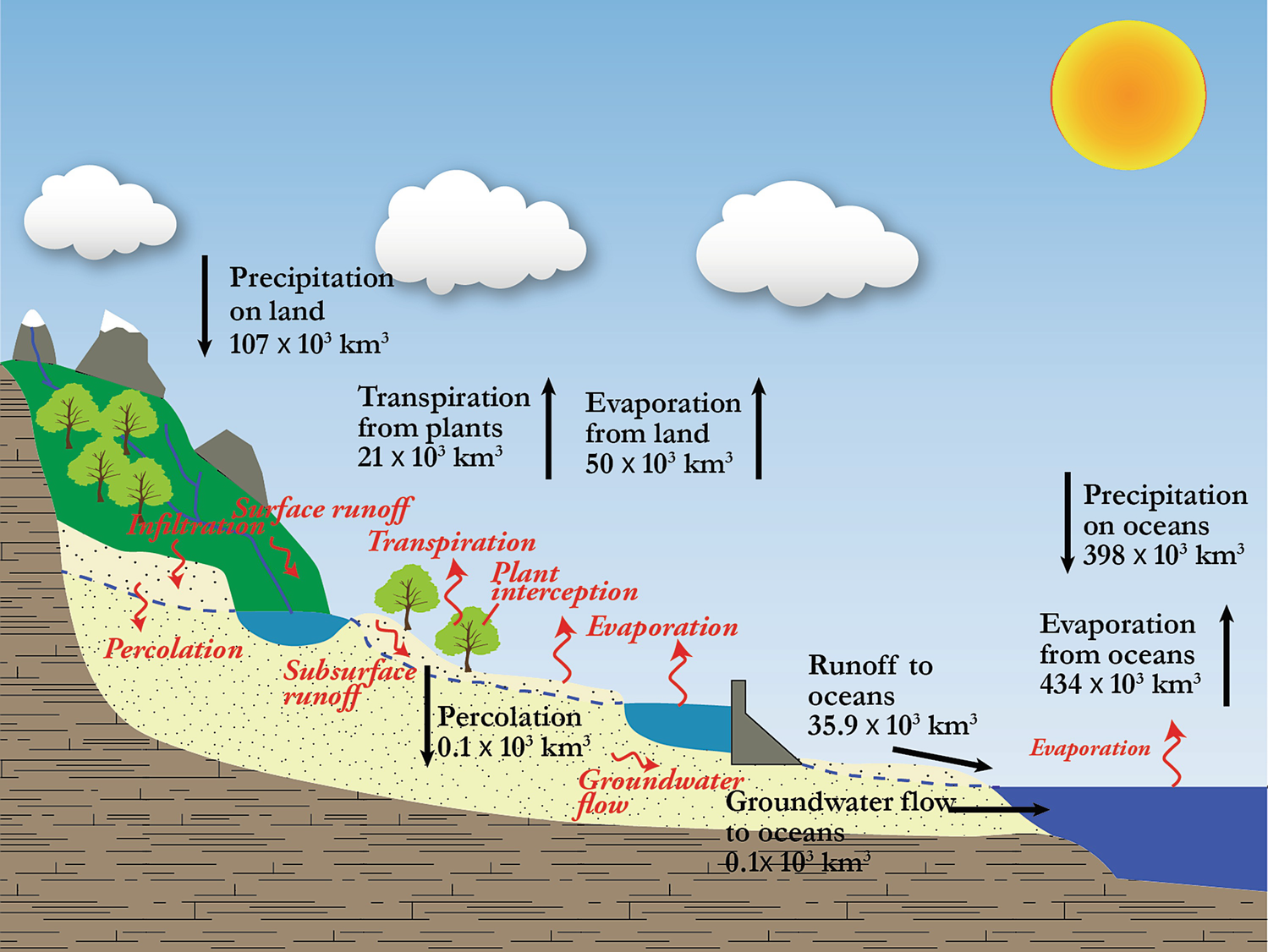



Hydrologic Cycle Springerlink
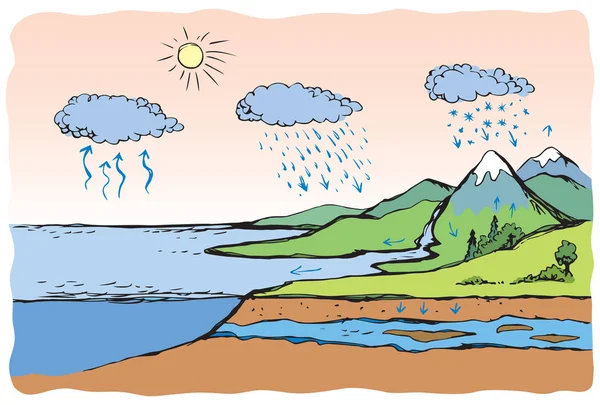




67 Hydrologic Cycle Vector Images Free Royalty Free Hydrologic Cycle Vectors Depositphotos
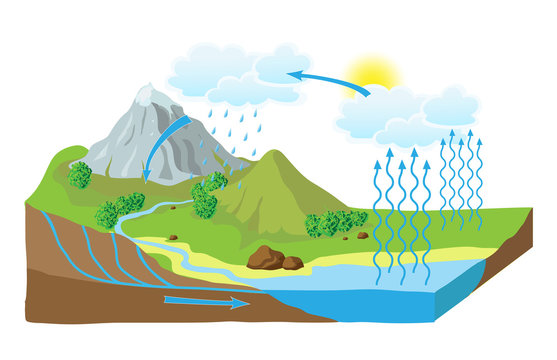



53 793 Best Water Cycle Images Stock Photos Vectors Adobe Stock
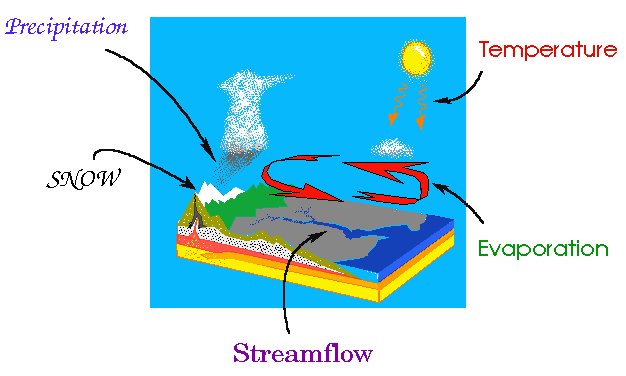



Description Of Hydrologic Cycle
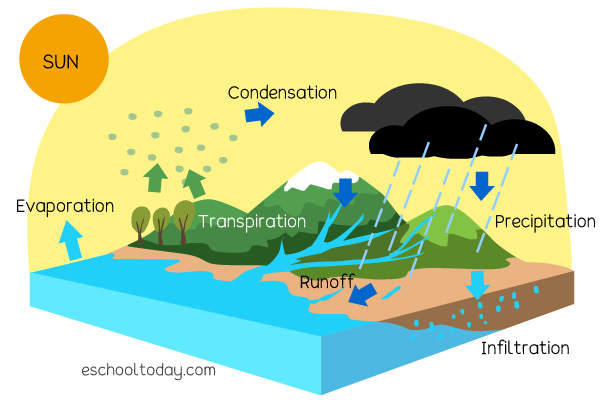



The Water Cycle Eschooltoday




Water Cycle Wikipedia
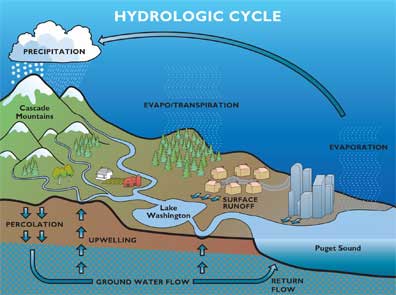



Hydrologic Cycle As An Ecological Function King County



Natural Water Cycle




Water Cycle Wikipedia
(145).jpg)



The Water Cycle Questions Answers Trivia Quiz Proprofs Quiz




The Hydrologic Cycle Water Cycle H2o Distributors




Water Cycle Management Wikipedia




Water Cycle Diagram Water Cycle Diagram Water Cycle Easy Drawings
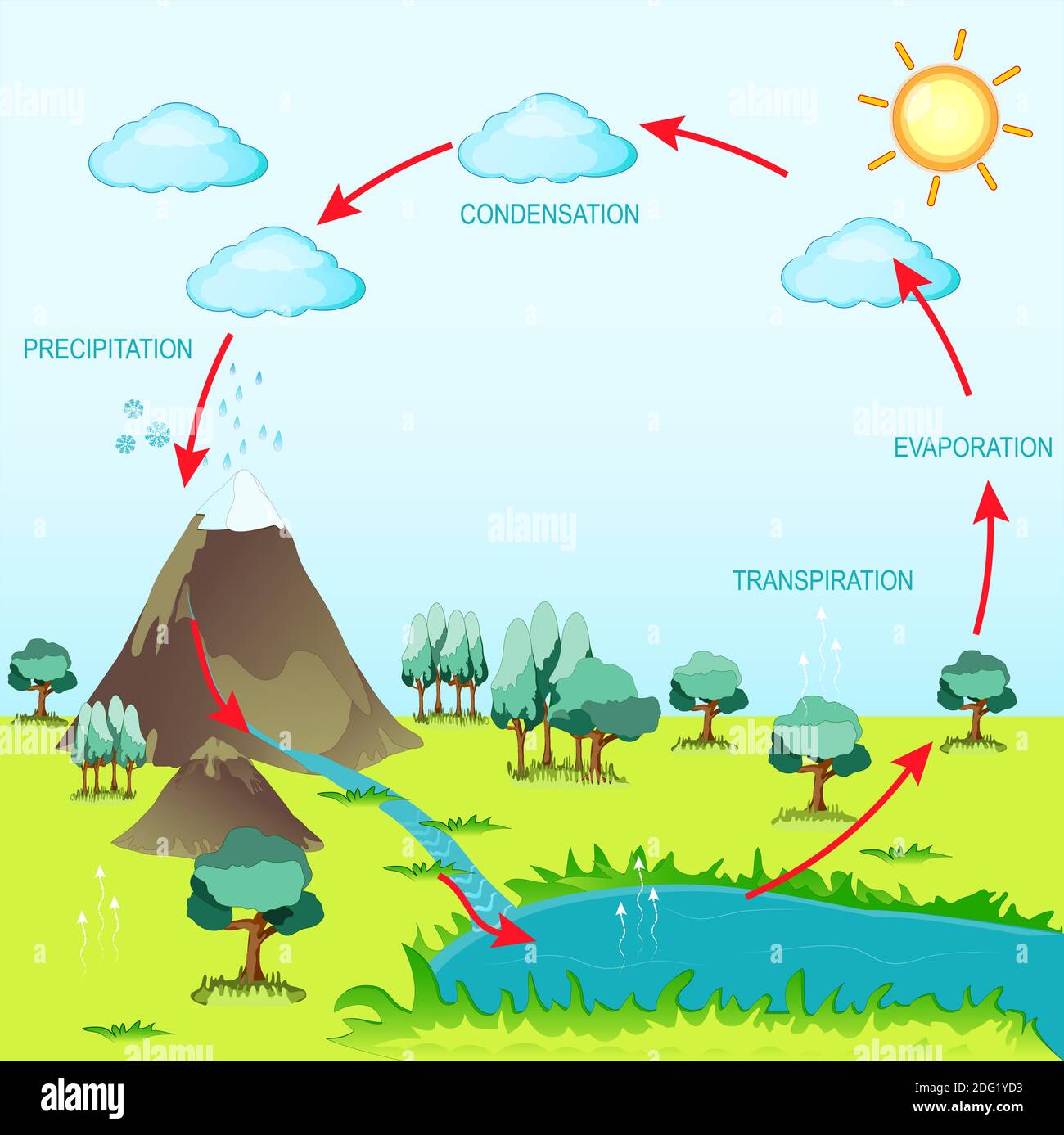



Water Cycle Diagram High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Water Cycle Water Cycle Pdf 161 Kb Water Cycle Diagram Cycle For Kids Water Cycle For Kids
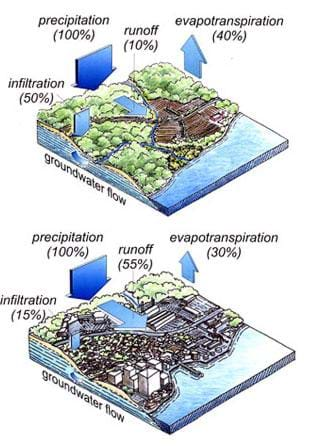



Natural And Urban Stormwater Water Cycles Lesson Teachengineering
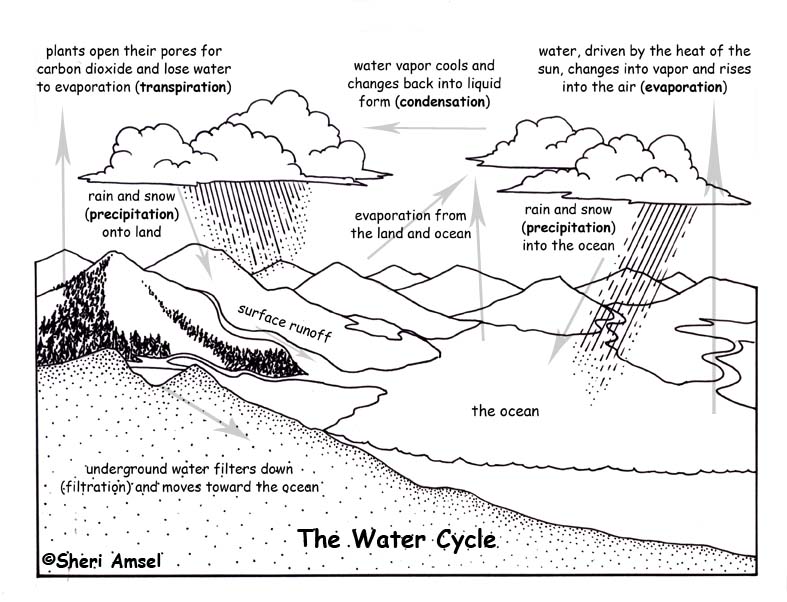



Water Cycle



Water Cycle



The Global Water Cycle What Can Isotopes Tell Us




Water Cycle Science Mission Directorate
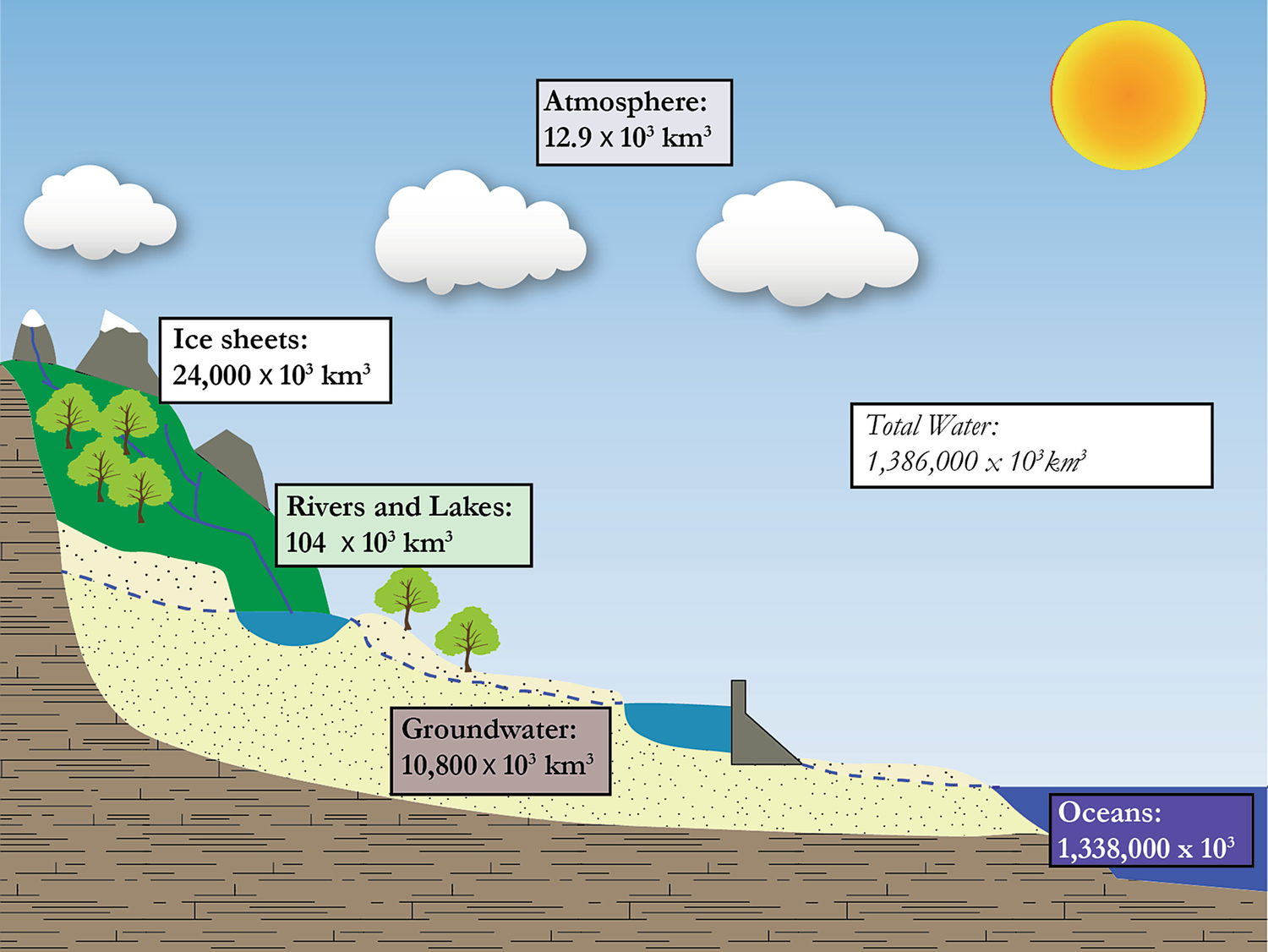



Hydrologic Cycle Springerlink
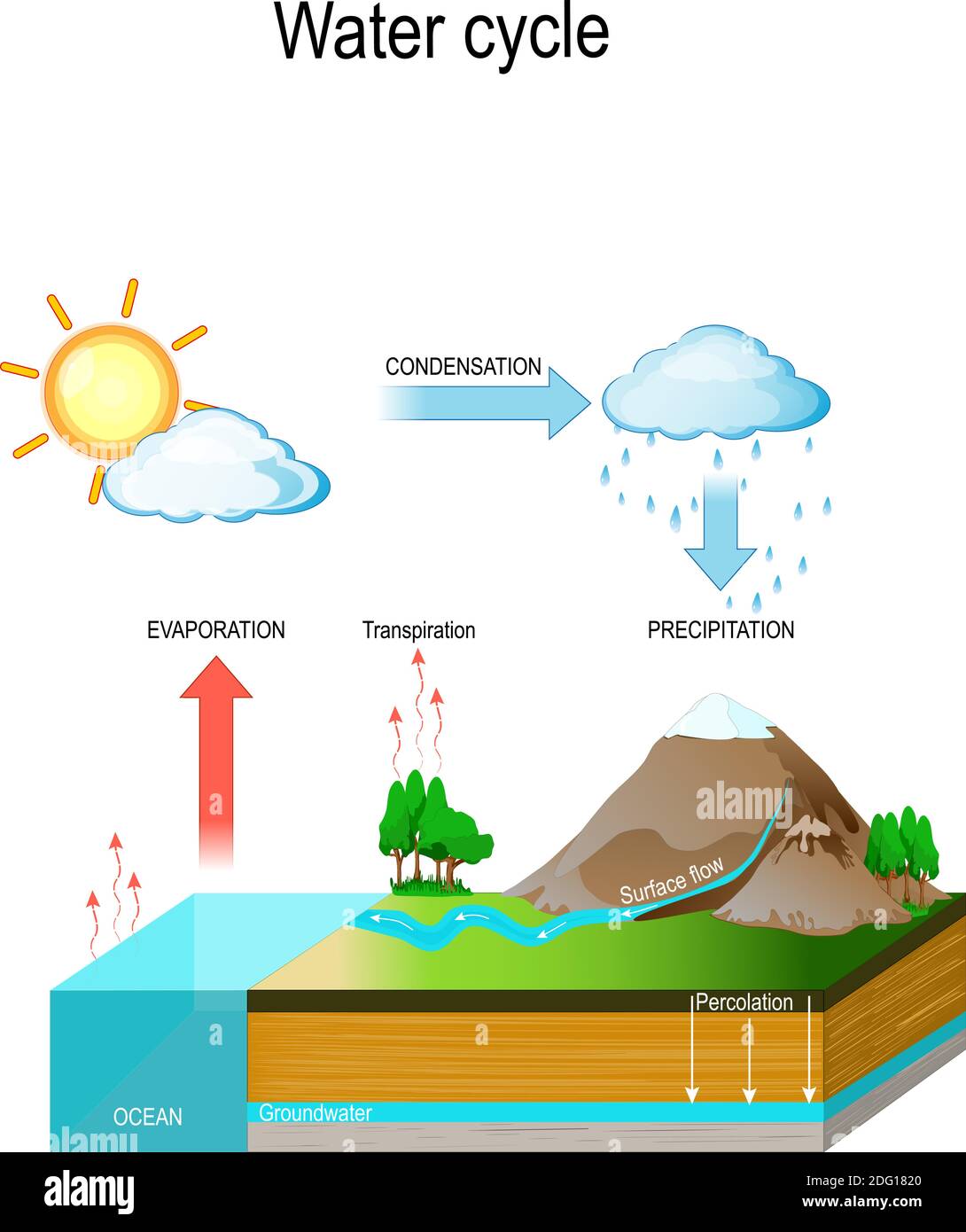



Water Cycle Diagram High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




A Comprehensive Study Of The Natural Water Cycle




Hydrological Cycle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Water Cycle Creation Com
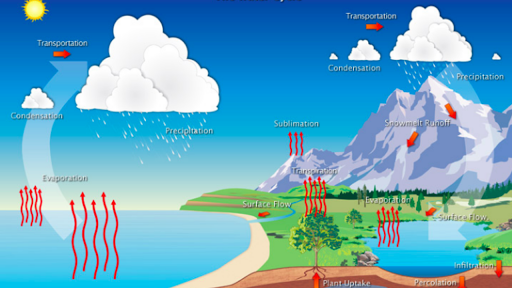



The Water Cycle Article Ecology Khan Academy
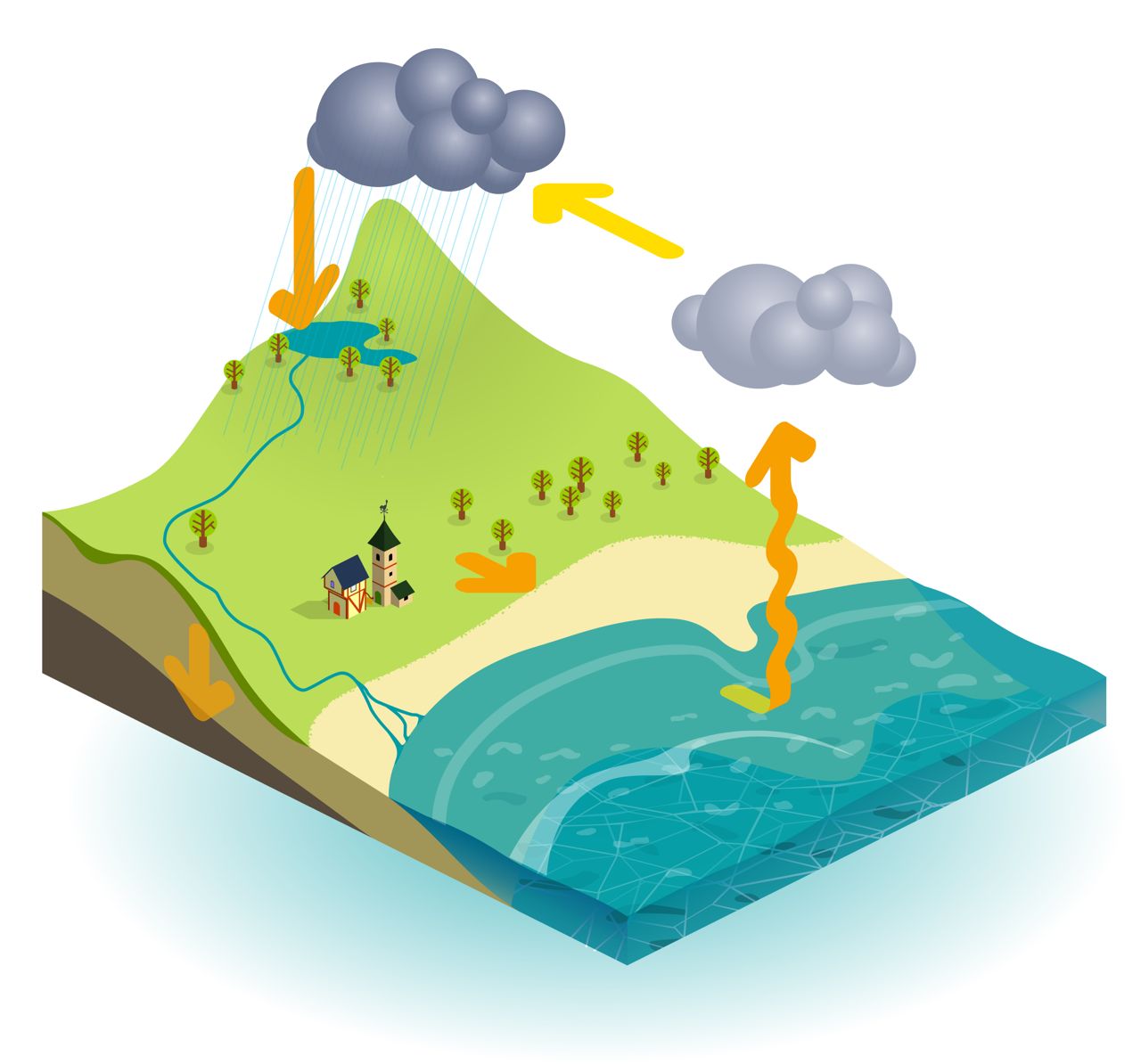



What Is The Water Cycle Theschoolrun
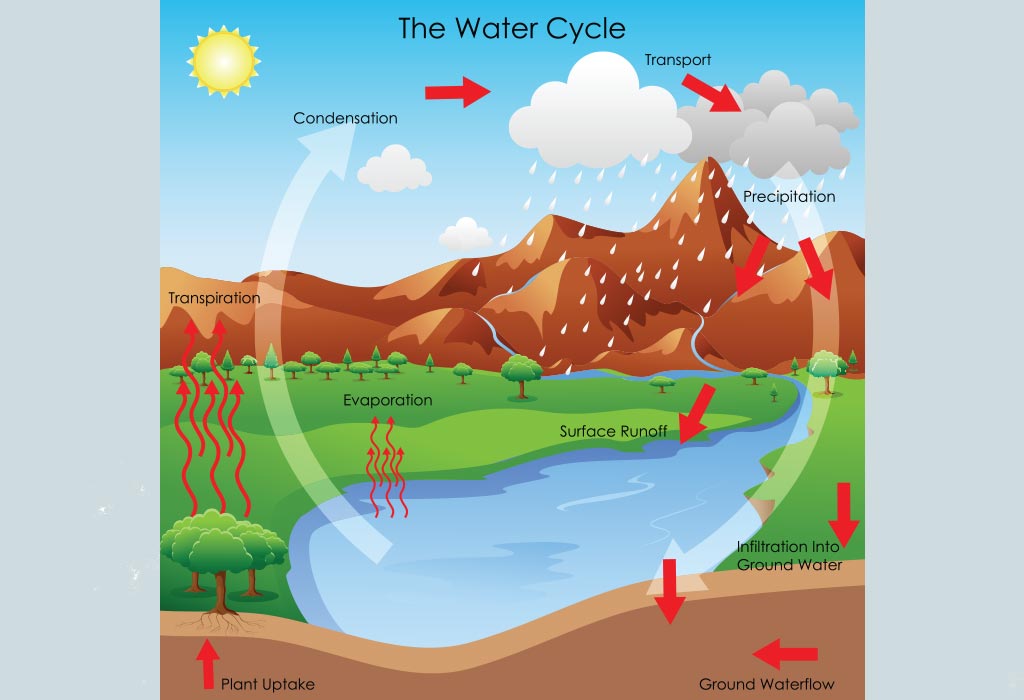



Water Cycle For Kids How It Works And Interesting Facts
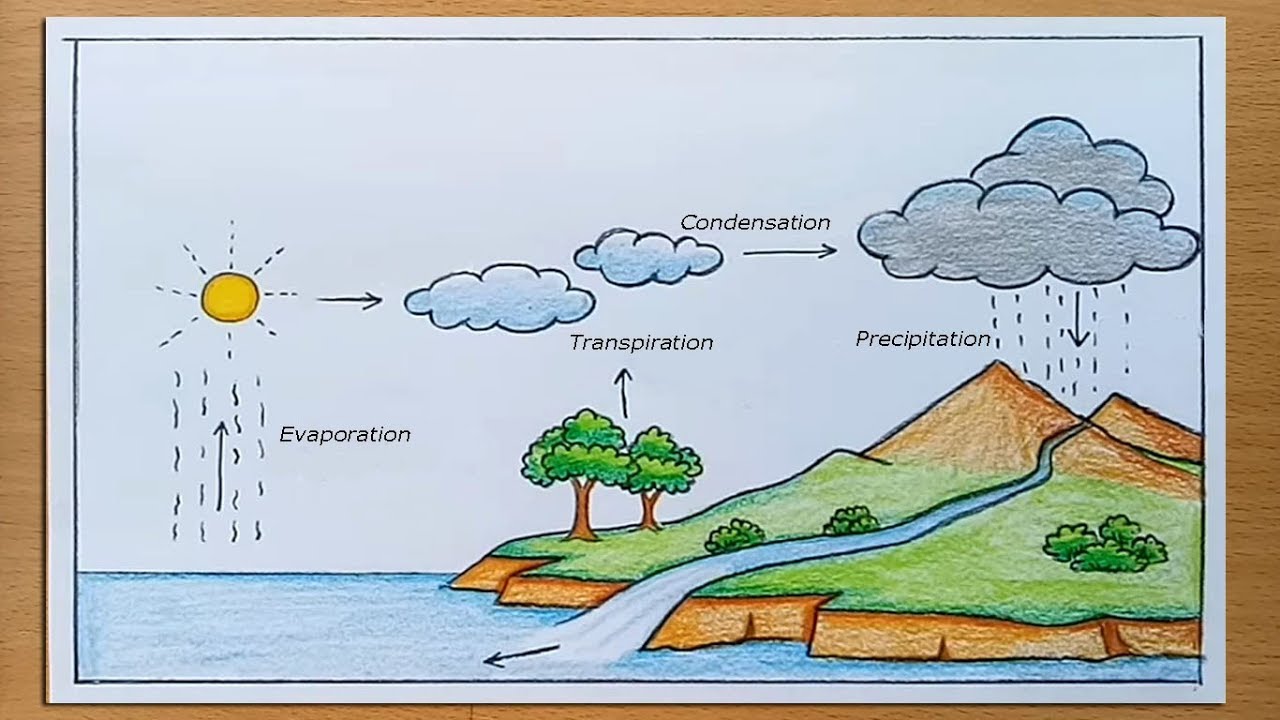



How To Draw Water Cycle Of A School Project Youtube



A Summary Of The Hydrologic Cycle Bringing All The Pieces Together
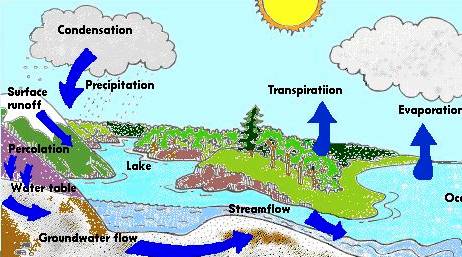



Envintenv5 The Water Cycle
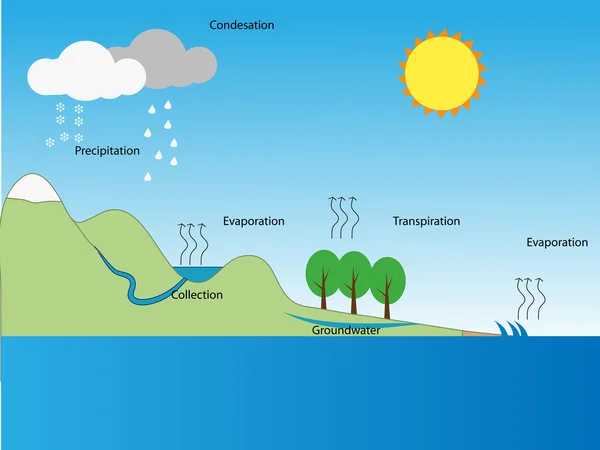



13 145 Water Cycle Vector Images Free Royalty Free Water Cycle Vectors Depositphotos
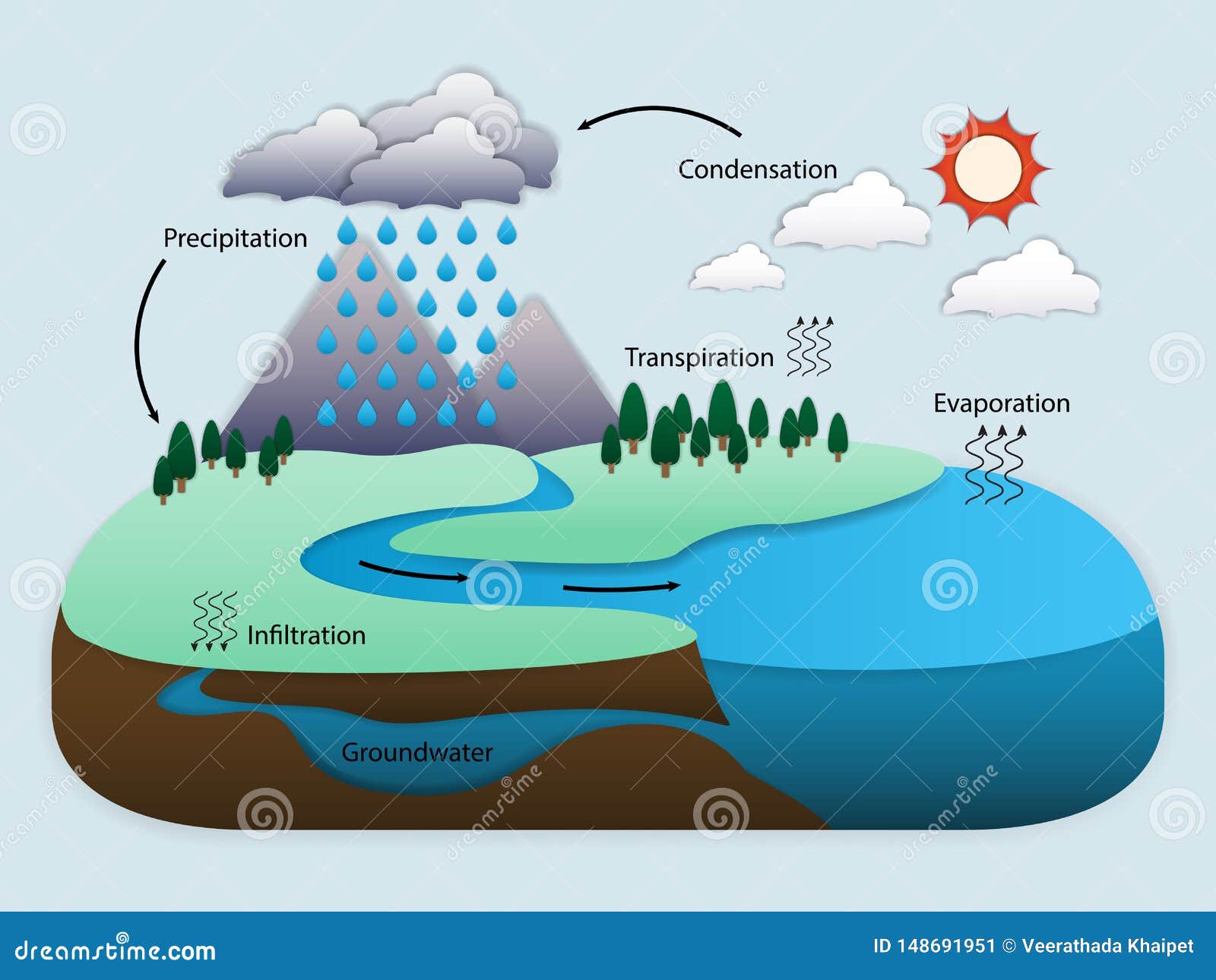



Water Cycle Diagram Stock Illustrations 592 Water Cycle Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime



Q Tbn And9gcqfm7sulmcemqq1uz3rzdaqsb6vvsmvu2nnrc5gmjhed9c6lpfp Usqp Cau
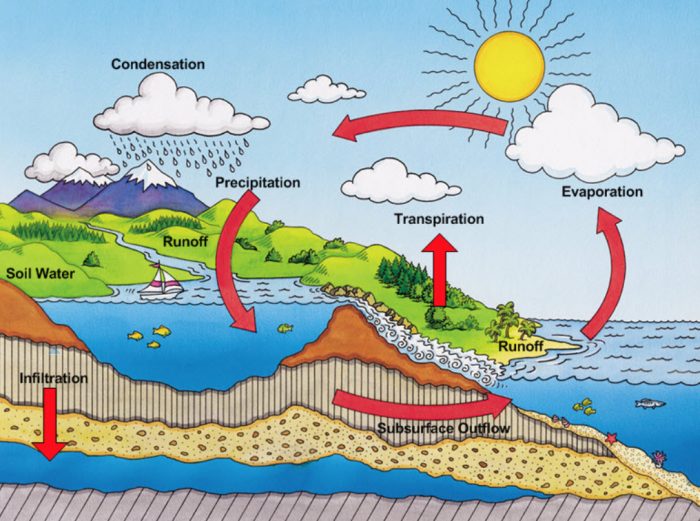



What Is Water Cycle In Short Know It Info
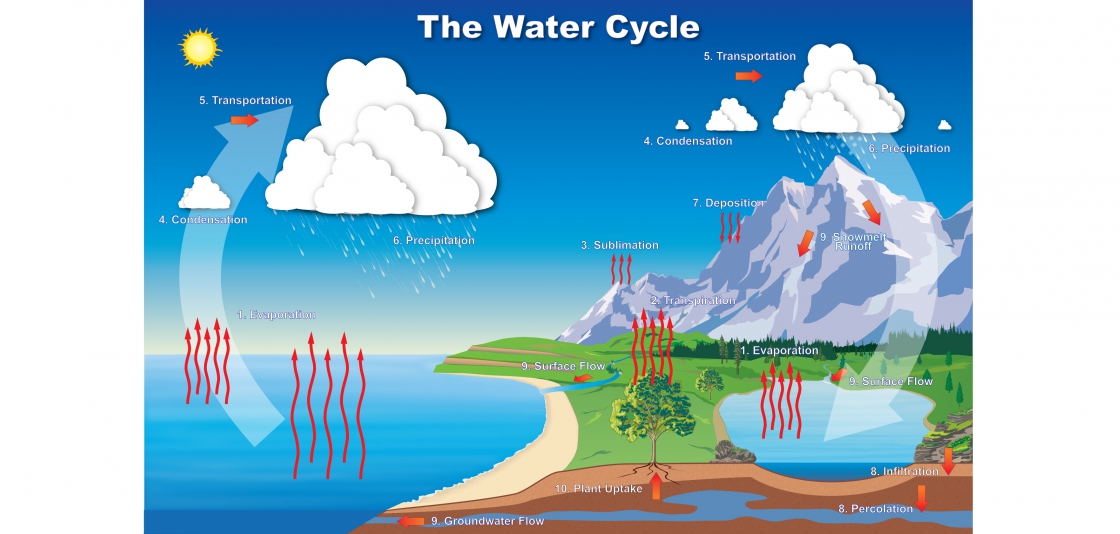



Water Cycle Colorado Water Knowledge Colorado State University




How To Draw Water Cycle Step By Step Water Cycle Drawing For Students Youtube
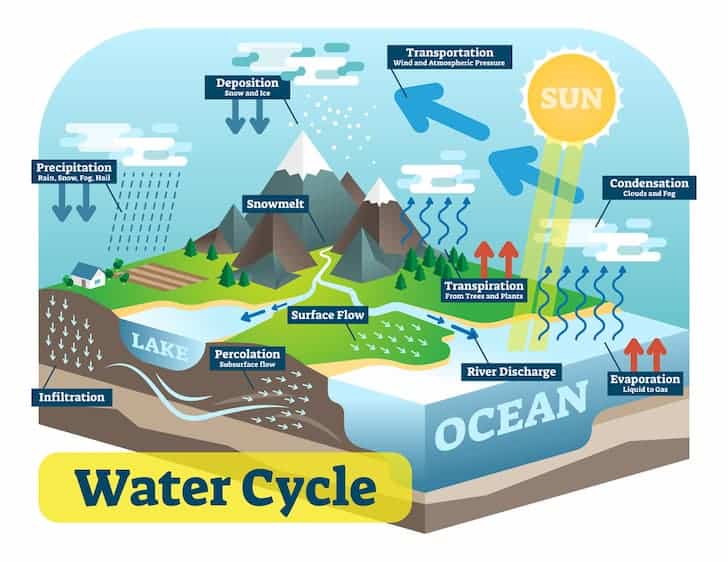



Different Stages And Importance Of The Water Cycle Conserve Energy Future



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿